Does ethanol have to be hurt by falling gas prices?
Jim Lane, editor and publisher of Biofuels Digest, is one person who thinks alternative fuels aren’t necessarily going to be hurt by the huge drop in the price of crude oil.
In a post on the Digest Jan. 6, Lane lays out the rather complicated case of why it doesn’t pay right now to be dumping your alternate-energy stocks. That’s been the reaction so far to anything related to the price of oil. But Lane says there are special aspects of alternatives like ethanol that will be affected in a different way.
In the first place, Lane notes that while crude oil prices have been falling, ethanol prices have been falling, too. Since last June, crude oil has fallen from $115 a barrel to under $50, a remarkable 60 percent drop. Yet ethanol has fallen as well, from $2.13 a gallon to $1.55 a gallon, a formidable 27 percent drop. This is due mainly to the falling price of corn, which has been at its lowest level in recent years. A bushel of corn fell over the same period from $4.19 a bushel to $3.78, a 10 percent drop. In this way, ethanol is only marginally dependent on the price of oil and can show its own price pattern.
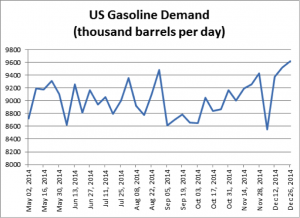
One thing worth noting is that there is a certain amount of elasticity in American driving. People tend to increase their driving range when the price of gasoline goes down. This is particularly true when it comes to taking vacations, which tend to be a long-term planning effort. If the price of gasoline stays down through next summer, people are more likely to increase gas consumption. The fact is that gasoline demand has actually reached its highest point in the last few months since the price of oil began to fall, as the following graph indicates:
Now drivers are required to include 10 percent ethanol in each gallon of gas. Therefore, ethanol has a fixed market. Driving has been declining in recent years, which is one reason that the Renewable Fuel Standard has been under fire – because the absolute amount of ethanol required has exceeded the 10 percent requirement in relation to the amount of gasoline consumed. Refiners and oil companies must buy this amount of ethanol. This is the reason the Environmental Protection Agency has been holding back on setting an RFS for 2014 — because the original amount prescribed was going to exceed the 10 percent figure. If people start taking advantage of lower gas prices and start consuming more gasoline, the amount of ethanol required will grow. “(W)e should be seeing a 2+% increase in gasoline demand, and that will take some pressure off the ethanol blend wall,” Lane writes. It might make EPA’s decision easier, if it ever gets around to setting a number.
Just to emphasize this point, an RIN — Renewable Index Number — is required by the EPA to prove that a refinery has been adding ethanol up to the 10 percent mark. The price of RINs has actually been rising as gas prices have fallen. As Lane writes: “Part of the reason that the ethanol market is holding up relatively well in tough times is the impact of the Renewable Fuel Standard, and its traded RIN system. RIN prices have jumped as oil prices have slumped — and a $0.76 increase in the RIN value of a gallon of fuel is a striking increase in value.”
So all is not dark for the future of alternatives. Ethanol’s place is secure, despite the fall in gasoline prices. Remember, it’s not that demand for gas is falling, but people are spending less for what they get. If methanol is given a chance, it might turn out to be more invulnerable, since it’s not tied to corn prices but to natural gas, which we seem to have in even greater abundance than oil. Electric cars also don’t lose their appeal, since much of their appeal is getting off gas entirely and unbuckling from the oil companies. It may not be time to abandon your stock in alternative energies quite yet.