Archive for year: 2015
Evolution of Alcohol Fuel Blends Towards a Sustainable Transport Energy Economy
by J.W.G. Turner and R.J. Pearson et al, Lotus Engineering
The authors of this research argue that since there isn’t enough E85 to power all the flex-fuel vehicles on the road, “the introduction of methanol (which can be made extremely simply and cheaply from natural gas) into gasoline-ethanol mixtures, can be used to create drop-in fuels equivalent to E85 and can bring the price of an alcohol-based fuel for spark-ignition engines down to less than that of gasoline.”
Tesla hits some speed bumps
Tesla’s stock was down around $200 again after its fourth-quarter report disclosed that neither its sales nor profits had met analysts’ expectations. At the same time, the company went into what one analyst called its “insane mode” as founder Elon Musk predicted that by 2025 the company’s market capitalization would reach $700 billion, matching the current value of Apple.
Analysts were scratching their heads as Musk’s vision seemed utterly at odds with the difficulties that are starting to pile up with Tesla’s ability to meet current goals. The company’s 2014 revenues rose to $3.2 billion, up from $2 billion the year before. However, expenses continued to mount, and losses widened from $74 million to $294 million last year. For the fourth quarter, Tesla delivered only 9,834 of the 12,000 cars it had predicted. Musk blamed the winter weather and customers’ holiday travel for the shortfall. A bigger disappointment has been sales in China, where Tesla sold only 120 cars in January. Musk has supposedly messed up by insisting that the cars be sold only by dealers, whereas the Chinese want anyone to sell them. He also says that concerns about home chargers and the lack of public charging stations have made it extremely difficult to crack China’s notoriously tough market. Musk now says that the company is now not counting on any sales in China to help it reach its goals.
But those goals are wildly ambitious. Musk told analysts that Tesla is anticipating a 30 percent increase in revenues per year for the next 10 years, which is the pace needed to put Tesla’s market value on par with Apple’s. “That would imply sales volume of well over 5 million vehicles per year,” Edward Niedermeyer wrote in Bloomberg View. “That would have Tesla surpassing the 2014 sales of such familiar names as Nissan, Honda and Fiat-Chrysler – at highly significant profit margins – within a decade.” Needless to say, Niedermeyer and many others find this prospect unlikely.
But Tesla isn’t standing still. It announced last week that it will produce a battery for home electricity storage. This will fold nicely with its partnership with SunCity, run by Musk’s cousin. People who install solar panels on their roofs will welcome a battery system that allows them to store electricity for times when the sun doesn’t shine. Just as solar seems to function best when distributed across a wide variety of users, so energy storage may ultimately work best when it is distributed over a wide variety of users.
Whether Tesla will be able to survive all this, however, is still an open question. The main threat to Musk’s vision seems to be coming now, not from predictable delays and bumps in the road, but from healthy competition from experienced automakers. Chevrolet has announced the Bolt, a successor to the Volt, which will be swinging right in Tesla’s wheelhouse – the $30,000 market for electric vehicles that can travel 200 miles or more on one charge.
General Motors has moved the introduction date up to 2017 (the same as the Tesla 3) and seems deadly serious about entering the EV market. “The Bolt EV concept is a game-changing electric vehicle designed for attainability, not exclusivity,” General Motors CEO Mary Barra said in a statement. “Chevrolet believes electrification is a pillar of future transportation and needs to be affordable for a wider segment of customers.”
Besides the Bolt, GM will have an improved version of the Volt, plus the $75,000 Cadillac ELR, a plug-in model. Daniel Miller of Motley Fool isn’t terribly impressed with any of these efforts, noting that the ELR has already had little success competing with Tesla’s Model S in the luxury-car category. “Because of that premium, first-mover brand image that Tesla created with its Model S, it’s hard to imagine how the Bolt will steal much of Tesla’s Gen 3 market in 2017, even if it is price-competitive,” Miller writes.
But if Tesla really has something to worry about, it’s the rumors that Apple, its Silicon Valley rival and the world’s largest company, is preparing a secret plan to enter the car market as well. Just this week it was revealed that Apple has a secret project employing 1,000 people to come up with some kind of concept car that will rival the Tesla Model 3.
“Apple has batted around the idea of developing a car for years,” reported Adam Satariano and Tim Higgins of Bloomberg Business. “Phil Schiller, Apple’s senior vice president of marketing, said in 2012 court testimony that executives discussed building a car even before it released the iPhone in 2007. Mickey Drexler, an Apple board member and head of J Crew Group Inc., also said in 2012 that Apple co-founder Steve Jobs had wanted to build a car.”
Apple has worked on batteries for the iPhone and iPad and also has a supply chain that could easily be applied to vehicles. “The mapping system it debuted in 2012 can be used for navigation. Last year, Apple also introduced CarPlay, a software system that integrates iTunes, mapping, messaging and other applications for use by automakers,” Satariano and Higgins wrote. Of course, that’s a long way from turning out thousands of vehicles, but Apple has invaded other businesses before. It basically knew nothing about the music business when it started on iTunes, and had no experience with telephones when it invented the smartphone.
In any case, even if Tesla finds itself in competition with much larger established companies – something Musk predicted at the start – it is revolutionizing the field of automobiles by making the electric car seem practical. Although Musk’s dream may prove to be overblown, he has certainly advanced the search for alternatives to the internal combustion engine.
Film asks U.S. to PUMP down the oil volume
“What can you expect from a movie that’s produced by a group whose advisers include a former CIA director, a onetime Shell Oil Co. president and a man who once headed the Rockefeller Foundation? If you answered, ‘a spirited defense of America’s oil industry,’ guess again.”
Angry about rising gas prices? Do something about it
Silly American driver. Did you think gas prices were going to stay low forever?
When we say low, we should really say “low,” with derisive air quotes, because gas prices never really got to what a historian would certify as “low” anyway, even after crude oil dropped 60 percent between June and January. As New York Times columnist David Leonhardt noted in late January, for 17 years — from the beginning of 1986 to the end of 2002 — gasoline averaged $1.87 a gallon.
But gasoline had soared so high over the past decade that a sudden drop late last year, which pushed prices down to $2 or less in many places, felt like a tax holiday.
Well, holiday season is officially over. Oil set another 2015 high on Tuesday, with Brent crude, the international benchmark, rising $1.13 to $62.53. The peak of the session, $63, was the highest level it’s reached since Dec. 18.
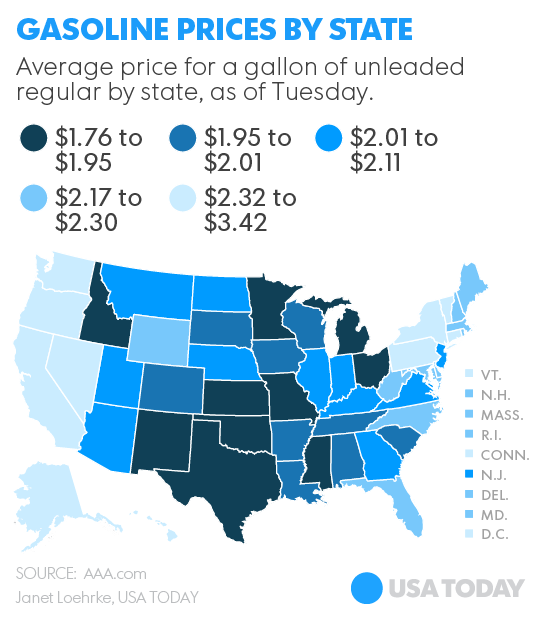
The surge — which caught analysts and experts off-guard, just as the plunge did before it — wasted no time in carrying over to the pump. According to the AAA’s Daily Fuel Gauge Report, the national average Tuesday was $2.259, up from $2.185 a week before and $2.076 a month before.
In some states, obviously, it’s climbed higher and faster than others. At my neighborhood station in Southern California, the price for basic 87-octane went from $2.39 to $2.85 in only a few weeks. At a different station across the intersection, the price has tracked an identical arc. I imagine the owners watching each other with infrared binoculars late at night, ready to hoist new digits onto their respective marquees when one rival dares to up the ante a dime.
Patrick DeHaan, senior petroleum analyst at Gas Buddy, wrote Monday:
“Motorists in California are getting a taste of the sourness that will hit across the country in a month or two as Los Angeles switches over to cleaner burning gasoline, followed by San Francisco in short order, with the rest of the nation making moves in the weeks and months ahead. I’m also starting to hear more frustration from motorists about rising prices- and while the concerns are well rooted, they should take solace that gas prices this summer are still expected to be some $1/gal lower than last summer.”
Raise your hand if you’re in the mood for some solace.
Drivers are more likely to feel confused and exasperated by the inexplicable price spikes and the baseless predictions.
If you’re angry about rising gas prices ebbing away at the money you thought you were saving last fall, you can do something about it: First, watch PUMP the movie, on Amazon, iTunes, DVD or at a public screening. Second, convince your friends to watch it, or volunteer to host a screening in your city. (Do you get the idea we want people to watch this important film?) Third, sign our petition urging fueling retailers to make alternative fuels, like E85, available to consumers.
Ending our reliance on oil as the only fuel option for vehicles is possible in the next few years, but only if we act. It sure beats complaining about the price of gas.
Georgia Aquarium CEO Michael Leven joins Fuel Freedom board of advisors
Michael Leven, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Georgia Aquarium, and a longtime supporter of philanthropic endeavors, has joined Fuel Freedom Foundation’s board of advisors.
Making the case for sustainable energy
Bloomberg and the Business Council for Sustainable Energy are not at all discouraged by the big drop in oil prices. In fact, they say that the move toward non-carbon-based energy is so strong now that it’s taking on an air of inevitability.
That was the conclusion of the third annual Sustainable Energy in America Factbook, released by the council last week and researched and published by Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF). The press conference, held in conjunction with the report’s release, featured an all-star lineup of industry experts, including David McCurdy, head of the American Gas Association; Tom Kiernan, CEO of the American Wind Energy Association; and Mark Wagner, vice president for government relations at Johnson Controls.
“America is in the midst of a sweeping energy transformation,” the report began. “New technologies and concerns about energy security and the future of the world’s climate are together driving rapid change in the U.S. energy economy. … Traditional energy sources are declining while natural gas, renewable energy and energy conservation are playing a larger role.”
On the possibilities of replacing gasoline — despite its cheaper price — the council was particularly optimistic about the future of electric cars. “Here’s why cheap oil won’t stop electric vehicles:”
“1. Since 2010 there’s been no relationship between gasoline price and electric vehicle sales, according to BNEF analyst Alejandro Zamorano Cadavid. Electric cars are still in the early-adopter phase, and someone paying $100,000 for a Tesla doesn’t care that gasoline costs a buck less per gallon.
“2. In Europe, gas taxes are so high that it makes the price of crude less important. If you’re in Norway, and gas drops from $10 a gallon to $9 a gallon, electric cars are still a deal.
“3. In China, the government is stepping up support for electric vehicles. Pollution has become a serious problem, and the Chinese are getting serious about fixing it. Plug-in sales are soaring.”
Of course, the council is taking a world perspective. The report mentions, for instance, that fossil-fuel subsidies outpace renewable-energy subsidies by 6 to 1. Most of those subsidies, however, are government edicts in developing nations that reduce the price of gasoline to consumers. In Venezuela, for example, gasoline is being sold at 2 cents per gallon. But this is left over from Hugo Chavez’s policies of using the country’s oil production to provide almost free gasoline to the people under the principle of “sharing the wealth.” This policy has proved disastrous, and the low price of world oil has practically bankrupted the country.
The same pattern has occurred in other countries, but low oil prices are proving to be a boon to governments. “First, a number of countries, including India and Indonesia, have used the price drop as cover to cut gasoline subsidies that were weighing town their budgets,” says the report. “Second, countries that include China have pocketed the savings from cheaper oil by increasing gasoline taxes to make up the difference.”
The pattern in the United States, where there is a freer market, has apparently been that cheaper gas prices are not cutting into the progress of plug-in cars and hybrids. They have risen to almost 2 percent of all car sales, after languishing well below 0.5 percent only three years ago. There may be a temporary drop now due to low gasoline prices, but the prices are not likely to stay down, and sales will probably bounce back. This is particularly true since both Tesla and GM are planning to introduce all-electrics to the mid-range market by 2017. Both companies are planning to market electrics in the $35,000 range, which will remove them from the “first-adopter” stage.
Of course, switching to electric doesn’t mean much if the electricity is producing the same old pollution, but there the Business Council says that the switch to cleaner natural gas — and particularly solar electricity — will make electric cars even more attractive. The council notes that oil plays very little role in the generation of electricity, and that electricity price are still going up, which makes solar electricity even more attractive. “Solar . . . will be the world’s biggest single source [of electricity] by 2050, according to the International Energy Agency.”
Although the report doesn’t mention it, improvements in cellulosic ethanol will revolutionize that market as well. And there is always the possibility that we may take advantage of our abundant natural-gas resources to convert gas to methanol, another cheap and clean substitute for gasoline.
Altogether, it does not appear that the temporary drop in oil prices is going to slow the effort to produce cleaner, cheaper energy that moves us away from dependence on foreign oil sources. That’s good news all around.
Alternative and renewable fuels: There is life after cheap gas!
 Some environmentalists believe that if you invest in and develop alternative replacement fuels (e.g., ethanol, methanol, natural gas, etc.) innovation and investment with respect to the development of fuel from renewables will diminish significantly. They believe it will take much longer to secure a sustainable environment for America.
Some environmentalists believe that if you invest in and develop alternative replacement fuels (e.g., ethanol, methanol, natural gas, etc.) innovation and investment with respect to the development of fuel from renewables will diminish significantly. They believe it will take much longer to secure a sustainable environment for America.
Some of my best friends are environmentalists. Most times, I share their views. I clearly share their views about the negative impact of gasoline on the environment and GHG emissions.
I am proud of my environmental credentials and my best friends. But fair is fair — there is historical and current evidence that environmental critics are often using hyperbole and exaggeration inimical to the public interest. At this juncture in the nation’s history, the development of a comprehensive strategy linking increased use of alternative replacement fuels to the development and increased use of renewables is feasible and of critical importance to the quality of the environment, the incomes of the consumer, the economy of the nation, and reduced dependence on imported oil.
There you go again say the critics. Where’s the beef? And is it kosher?
Gasoline prices are at their lowest in years. Today’s prices convert gasoline — based on prices six months ago, a year ago, two years ago — into, in effect, what many call a new product. But is it akin to the results of a disruptive technology? Gas at $3 to near $5 a gallon is different, particularly for those who live at the margin in society. Yet, while there are anecdotes suggesting that low gas prices have muted incentives and desire for alternative fuels, the phenomena will likely be temporary. Evidence indicates that new ethanol producers (e.g., corn growers who have begun to blend their products or ethanol producers who sell directly to retailers) have entered the market, hoping to keep ethanol costs visibly below gasoline. Other blenders appear to be using a new concoction of gasoline — assumedly free of chemical supplements and cheaper than conventional gasoline — to lower the cost of ethanol blends like E85.
Perhaps as important, apparently many ethanol producers, blenders and suppliers view the decline in gas prices as temporary. Getting used to low prices at the gas pump, some surmise, will drive the popularity of alternative replacement fuels as soon as gasoline, as is likely, begins the return to higher prices. Smart investors (who have some staying power), using a version of Pascal’s religious bet, will consider sticking with replacement fuels and will push to open up local, gas-only markets. The odds seem reasonable.
Now amidst the falling price of gasoline, General Motors did something many experts would not have predicted recently. Despite gas being at under $2 in many areas of the nation and still continuing to decrease, GM, with a flourish, announced plans, according to EPIC (Energy Policy Information Agency), to “release its first mass-market battery electric vehicle. The Chevy Bolt…will have a reported 200 mile range and a purchase price that is over $10,000 below the current asking price of the Volt.It will be about $30,000 after federal EV tax incentives. Historically, although they were often startups, the recent behavior of General Motor concerning electric vehicles was reflected in the early pharmaceutical industry, in the medical device industry, and yes, even in the automobile industry etc.
GM’s Bolt is the company’s biggest bet on electric innovation to date. To get to the Bolt, GM researched Tesla and made a $240 million investment in one of its transmissions plan.
Maybe not as media visible as GM’s announcement, Blume Distillation LLC just doubled its Series B capitalization with a million-dollar capital infusion from a clean tech seed and venture capital fund. Tom Harvey, its vice president, indicated Blume’s Distillation system can be flexibly designed and sized to feedstock availability, anywhere from 250,000 gallons per year to 5 MMgy. According to Harvey, the system is focused on carbohydrate and sugar waste streams from bottling plants, food processors and organic streams from landfill operations, as well as purpose-grown crops.
The relatively rapid fall in gas prices does not mean the end of efforts to increase use of alternative replacement fuels or renewables. Price declines are not to be confused with disruptive technology. Despite perceptions, no real changes in product occurred. Gas is still basically gas. The change in prices relates to the increased production capacity generated by fracking, falling global and U.S. demand, the increasing value of the dollar, the desire of the Saudis to secure increased market share and the assumed unwillingness of U.S. producers to give up market share.
Investment and innovation will continue with respect to alcohol-based alternative replacement and renewable fuels. Increasing research in and development of both should be part of an energetic public and private sector’s response to the need for a new coordinated fuel strategy. Making them compete in a win-lose situation is unnecessary. Indeed, the recent expanded realization by environmentalists critical of alternative replacement fuels that the choices are not “either/or” but are “when/how much/by whom,” suggesting the creation of a broad coalition of environmental, business and public sector leaders concerned with improving the environment, America’s security and the economy. The new coalition would be buttressed by the fact that Americans, now getting used to low gas prices, will, when prices rise (as they will), look at cheaper alternative replacement fuels more favorably than in the past, and may provide increasing political support for an even playing field in the marketplace and within Congress. It would also be buttressed by the fact that increasing numbers of Americans understand that waiting for renewable fuels able to meet broad market appeal and an array of household incomes could be a long wait and could negatively affect national objectives concerning the health and well-being of all Americans. Even if renewable fuels significantly expand their market penetration, their impact will be marginal, in light of the numbers of older internal combustion cars now in existence. Let’s move beyond a win-lose “muddling through” set of inconsistent policies and behavior concerning alternative replacement fuels and renewables and develop an overall coordinated approach linking the two. Isaiah was not an environmentalist, a businessman nor an academic. But his admonition to us all to come and reason together stands tall today.

