China emerges as a global leader in EVs
It’s an ill wind that doesn’t blow somebody some good, and it’s an ill pollution day that doesn’t have an upside somewhere.
It’s an ill wind that doesn’t blow somebody some good, and it’s an ill pollution day that doesn’t have an upside somewhere.
Fuel Freedom Foundation chairman Yossie Hollander delivered the keynote address Nov. 16 at a discussion hosted by the Hudson Institute in Washington, D.C., called “U.S.-China Energy Cooperation: Risks, Opportunities, and Solutions.”
With the price of oil down from about $115 to $63 since last June, the impression has been created that the auto world is once again in the hands of the oil industry, and that the gasoline engine is here to stay.
But this week at the Bloomberg New Energy Finance Conference, there was the distinct impression that alternatives to the gasoline engine are moving up so fast that within another five years we may see big changes. Bloomberg Business wrote that the result is “Future transport is likely to look a lot different than what the major oil companies are fueling now. Instead of biofuels such as ethanol and green diesel making the internal-combustion engine fit into a world with greenhouse gas limits, wholesale new solutions are coming fast.”
“Where we are is in an age of plenty,” Michael Liebreich, BNEF’s founder, told Bloomberg. “We have cheap oil, cheap gas, cheap renewables. You do have an abundance of supply in a way you haven’t had for decades. We also are in an age of competition.”
The biggest piece of news is that gasoline consumption has leveled off over the last decade and now is lower than it was in 2006. This is a remarkable development that no one knows quite how to explain. Part of it may be the lingering recession. Fleet mileage improvement has definitely made a difference, improving from 24.5 in 2001 to 31.6 today, a dramatic surge of 29 percent in 13 years. The Age of the Hummer is over, and people are being more selective in shopping for better mileage, even as the vehicles improve.
But Bloomberg Energy sees alternatively fueled vehicles also making headway in a way that is just becoming visible. Electric car sales have quintupled over the last four years, although they did start at a very low base. But battery prices are coming down as rapidly as solar-panel prices, which means that they soon will be in a range where the average American can afford them. Tesla’s 2017 debut of the Model 3, priced in the $35,000 range, is going to be a real turning point, if everything goes right.
Also coming along rapidly is the hydrogen car, which the Japanese auto industry has chosen as its alternative to gasoline. Toyota and Honda are just beginning to market their models in Japan, and BNEF anticipates there will be 4,200 on the road in Japan by 2018. But California is another big potential market, and sales are scheduled to begin there sometime late this year. The California Legislature has responded by expanding the Hydrogen Highway initiated by former government Arnold Schwarzenegger, making it easier for drivers to refuel.
Of course, all these predictions are taking place on a world scale, and there the progress may be even more rapid than in the United States. One thing Tesla discovered in its relatively abortive attempt to crack the Chinese market is that China already has a thriving electric-car industry. The cars, moreover, are not scaled-down versions of powerful sports cars but slow-moving vehicles that have been designed from the ground up.
In an article in Forbes last week, Jack Perkowski outlined what he called “China’s other electric vehicle industry:”
While the global automotive giants struggle to find a winning formula for electric vehicles, approximately 100 manufacturers in China have already identified a large potential market undiscovered by the traditional players. The common problems faced by EV automakers — high cost, driving range, and the availability of charging stations — are not issues for these manufacturers because their target customers are satisfied with low-speed and limited range EVs, as long as they provide affordable transportation. In 2014, 400,000 so-called ‘low-speed’ EVs were sold in China, compared to only 84,000 conventional all electric and hybrid electric vehicles.
To get a glimpse of the size of China’s potential market, consider this: China is already the world’s largest vehicle market, accounting for 25 percent of all vehicles manufactured globally. Yet there is only 1 vehicle per 10 people in China, whereas in the United States there are 8 for every 10 – more than one vehicle for every person of driving age. China also has another huge market for other electric vehicles. It has sold 90 million motorcycles and 120 million electric bicycles.
Estimates are that China now has a million such low-speed EVs on the road now and might reach 3 million by 2020. These cars can do about 48 miles per hour and are used for short runs around town in smaller cities, so range is not a problem. They are doing wonders for air pollution. Manufacture only began in 2006, and already some provincial governments are starting to write requirements that they be preferred to the older gasoline types.
Surprisingly, the only government entity that has been slow to embrace the low-speed EVs is the national government in Beijing. The Central Government has not counted these EVs is their official automotive statistics and is only now starting to write regulations on how crash-worthy they must be and on what roads they will be allowed to travel.
Perkowski concludes: “Low-speed EVs may not fit the stereotype of today’s modern passenger car, but in China, where incomes remain low for a large part of the country’s population, affordability often trumps those values held dear in more developed countries.”
Could China’s low-speed EVs find a market in the United States? It’s certainly possible. In any case, the anti-gasoline revolution may be coming in ways we did not anticipate.
 Turn on your local news every night and you’ll need a sleeping pill to get some rest. The format and content is the same around the country: a lot of tragic crime — ranging from sexual harassment, robbery and shootings — for about ten minutes; local sports for about 5 minutes; what seems like ten minutes of intermittent advertising; silly banter between two or more anchors for two minutes; and a human-interest story to supposedly lighten up your day at the very end of the show — likely about a dog and cat who have learned to dance together or a two-year-old child who already knows how to play Mozart. You get the picture!
Turn on your local news every night and you’ll need a sleeping pill to get some rest. The format and content is the same around the country: a lot of tragic crime — ranging from sexual harassment, robbery and shootings — for about ten minutes; local sports for about 5 minutes; what seems like ten minutes of intermittent advertising; silly banter between two or more anchors for two minutes; and a human-interest story to supposedly lighten up your day at the very end of the show — likely about a dog and cat who have learned to dance together or a two-year-old child who already knows how to play Mozart. You get the picture!
Local news, as presently structured, is not about to send you to sleep feeling good about humanity, never mind your community or nation. National news is really only marginally better. Again, the first ten minutes, more often than not, are about environmental disasters in the nation or the world — hurricanes, volcanoes, cyclones and tornadoes. The second ten minutes includes maybe one or two tragically laced stories, more often than not, about fleeing refugees, suicide bombings, dope and dopes and conflict. Finally, at the end of the program, for less than a minute or two, there is generally a positive portrayal of a 95-year-old marathon runner or a self-made millionaire who is now single-handedly funding vaccinations for kids in Transylvania after inventing a three-wheeled car that will never need refueling and can seat twenty-five people.
Maybe this is how the world is! We certainly need to think about the problems and dangers faced by our communities, the nation and its citizens. Every now and then, Americans complain about the media’s emphasis on bad news. But their complaints are rarely recorded precisely in surveys of viewership. We criticize the primary emphasis on bad news, but seem to watch it more than good news. Somewhat like football, we know it causes emotional and physical injuries to players, but support it with the highest TV ratings and attendance numbers.
Jimmy Fallon, responding to the visible (but likely surface) cry for more good news, has added a section to The Tonight Show. He delivers fake, humorous news, which is, at times, an antidote to typical TV or cable news shows. Perhaps John Oliver, a rising comedian on HBO, does it even better. He takes real, serious news about human and institutional behavior that hurts the commonweal and makes us laugh. In the process, we gain insight.
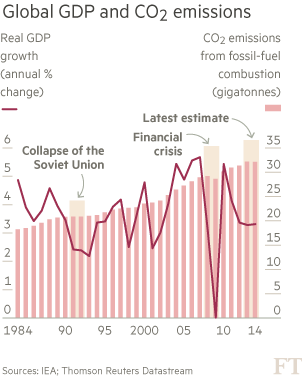
This week’s news about carbon dioxide emissions “stalling” in 2014 for the first time in 40 years appeared in most newspapers (I am a newspaper junkie) led by The New York Times and the Financial Times. It seemed like good news! Heck, while the numbers don’t reflect a decline in carbon emissions, neither do they illustrate an increase. Let’s be thankful for what we got over a two-year period (in the words of scientists — stability, or 32.3bn tons a year).
But don’t submit the carbon stability numbers to Jimmy Fallon just yet. It’s much too early for a proposed new segment on The Tonight Show called “Real as Opposed to Fake, Good News.” Too much hype could convince supporters of efforts to slow down climate change that real progress is being made. We don’t know yet. Recent numbers only reflect no carbon growth from the previous year over a 12-month period. The numbers might be only temporary. They shouldnt lessen the pressure to define a meaningful fair and efficient strategy to lower GHG. If this occurs, yesterday’s good news will become a real policy and environmental problem for the U.S. and the world for many, many tomorrows.
I am concerned that the stability shown in the carbon figures may be related to factors that might be short lived. Economists and the media have attributed the 2014 plateau to decreases in the rate of growth of China’s energy consumption and new government policies, as well as regulations on economic growth in many nations (e.g., requirements for more energy-efficient buildings and the production of more fuel-efficient vehicles), the growth of the renewable energy sector and a shift to natural gas by utilities.
Truth be told, no one appears to have completed a solid factor analysis just yet. We don’t really know whether what occurred is the beginning of a continuous GHG emission slowdown and a possible important annual decrease.
Many expert commentators hailed the IEA’s finding, including its soon-to-be new director, Dr. Fatih Birol. He indicated that this is “a very welcome surprise…for the first time, greenhouse gas emissions are decoupling from economic growth.”
Yet, most expert commentators suggest we should be careful. They noted that the data, while positive, is insufficient to put all our money on a bet concerning future trends. For example, Hal Harvey, head of Energy Innovation, indicated, “one year does not a trend make.”
Many articles responding to the publication of the “carbon stall” story, either implicitly or explicitly, suggested that to sustain stability and move toward a significant downward trend requires a national, comprehensive strategy that includes the transportation sector. It accounts for approximately 17 percent of all emissions, probably higher, since other categories such as energy use, agriculture and land use have murky boundaries with respect to content. Indeed, a growing number of respected environmental leaders and policy analysts now include vehicle emissions as well as emissions from gasoline production and distribution as a “must lower” part of a needed comprehensive national, state and local set of emission reduction initiatives, particularly,if the nation is to meet temperature targets. Further, there is an admission that is becoming almost pervasive: that renewable fuels and renewable fuel powered vehicles, while supported by most of us, are not yet ready for prime time.
While ethanol, methanol and biofuels are not without criticism as fuels, they and other alternative fuels are better than gasoline with respect to emissions. For example, the GREET Model used by the federal government indicates that ethanol (E85) emits 22.4 percent less GHG emissions (grams per mile) when compared to gasoline (E10). The calculation is based on life-cycle data. Other independent studies show similar results, some a higher, others a lower percent in reductions. But the important point is that there is increased awareness that alternative fuels can play a role in the effort to tamp down GHG.
So why, at times, are some environmentalists and advocates of alternative fuels at loggerheads. I suspect that it relates to the difference between perfectibility and perfection. Apart from those in the oil industry who have a profit at stake in oil and welcome their almost-monopoly status concerning retail sales of gasoline, those who fear alternatives fuels point to the fact that they still generate GHG emissions and the assumption, that, if they become competitive, there will be less investment in research and development of renewables. Yes! Alternative fuels are not 100 percent free of emissions. No! Investment in renewables will remain significant, assuming that the American history of innovation and investment in transportation is a precursor of the future.
Putting America on the path to significant emission reduction demands a strong coalition between environmentalists and alternative fuel advocates. Commitments need to be made by public, private and nonprofit sectors to work together to implement a realistic comprehensive fuel policy; one that views alternative fuels as a transitional and replacement fuel for vehicles and that encompasses both alternative fuels and renewables. Two side of the same policy and behavior coin. President Franklin Roosevelt, speaking about the travails of the depression, once said, “All we have to fear is fear itself.” His words fit supporters of both alternative fuels and renewables. Let’s make love, not war!
The reaction to President Obama’s climate-change deal with Chinese President Xi Jinping, among congressional Republicans, was swift and negative. The prevailing sentiment is that China didn’t give up as much in the bargain as the U.S., and that China isn’t likely to live up to its end of the agreement anyway.
But Mother Jones magazine quotes some experts on U.S.-China relations, and they say China is indeed serious about cutting greenhouse-gas emissions.
MJ’s James West writes:
So I asked experts on US-China relations to explain why this deal was so attractive to the leaders of two countries that have historically locked horns over everything from human rights to lingerie imports. Here’s their explanation of why China really does want to want to act on climate change, and why the bargain makes sense for President Barack Obama, as well:
China has to act on air pollution. If it doesn’t, the country risks political instability. Top Republicans have slammed the US-China deal as ineffective and one-sided. “China won’t have to reduce anything,” complained Sen. Jim Inhofe (Okla.) in a statement, adding that China’s promises were “hollow and not believable.”
But the assumption that China won’t try to live up to its end of the bargain misses the powerful domestic and global incentives for China to take action. The first, and most pressing, is visible in China’s appalling air quality. President Xi Jinping needs to act now, says Jerome A. Cohen, a leading Chinese law expert at New York University. Why? Because “the environment—not only the climate—is the most serious domestic challenge he confronts.”
President Obama and Chinese President Xi Jinping announced a milestone climate-change agreement in Beijing today, under which both countries would reduce greenhouse-gas emissions to meet certain targets.
A major goal of the agreement, which still needs to be formalized, is to spur other nations to reduce their own carbon output.
But the deal already is coming under criticism: As The New York Times reports, at least one climate-change expert says China could do more on its end; the country is vowing to cut off peak emissions only at “around” the year 2030.
Republicans in Congress were swift to criticize the deal. As The Hill notes, House Speaker John Boehner of Ohio issued a statement denouncing the deal as potentially harmful to the cheap energy that middle-class families rely on.
“This announcement is yet another sign that the president intends to double down on his job-crushing policies no matter how devastating the impact for America’s heartland and the country as a whole,” the statement said.
“It’s a puzzlement,” said the King to Anna in “The King and I,” one of my favorite musicals, particularly when Yul Brynner was the King. It is reasonable to assume, in light of the lack of agreement among experts, that the Chief Economic Adviser to President Obama and the head of the Federal Reserve Bank could well copy the King’s frustrated words when asked by the president to interpret the impact that the fall in oil and gasoline prices has on “weaning the nation from oil” and on the U.S. economy. It certainly is a puzzlement!
What we believe now may not be what we know or think we know in even the near future. In this context, experts are sometimes those who opine about economic measurements the day after they happen. When they make predictions or guesses about the behavior and likely cause and effect relationships about the future economy, past experience suggests they risk significant errors and the loss or downgrading of their reputations. As Walter Cronkite used to say, “And that’s the way it is” and will be (my addition).
So here is the way it is and might be:
1. The GDP grew at a healthy rate of 3.5 percent in the third quarter, related in part to increased government spending (mostly military), the reduction of imports (including oil) and the growth of net exports and a modest increase in consumer spending.
2. Gasoline prices per gallon at the pump and per barrel oil prices have trended downward significantly. Gasoline now hovers just below $3 a gallon, the lowest price in four years. Oil prices average around $80 a barrel, decreasing by near 25 percent since June. The decline in prices of both gasoline and oil reflects the glut of oil worldwide, increased U.S. oil production, falling demand for gasoline and oil, and the likely desire of exporting nations (particularly in the Middle East) to protect global market share.
Okay, what do these numbers add up to? I don’t know precisely and neither do many so-called experts. Some have indicated that oil and gas prices at the pump will continue to fall to well under $80 per barrel, generating a decline in the production of new wells because of an increasingly unfavorable balance between costs of drilling and price of gasoline. They don’t see pressure on the demand side coming soon as EU nations and China’s economies either stagnate or slow down considerably and U.S. economic growth stays below 3 percent annually.
Other experts (do you get a diploma for being an expert?), indicate that gas and oil prices will increase soon. They assume increased tension in the Middle East, the continued friction between the West and Russia, the change of heart of the Saudis as well as OPEC concerning support of policies to limit production (from no support at the present time, to support) and a more robust U.S. economy combined with a relaxation of exports as well as improved consumer demand for gasoline,
Nothing, as the old adage suggests, is certain but death and taxes. Knowledge of economic trends and correlations combined with assumptions concerning cause and effect relationships rarely add up to much beyond clairvoyance with respect to predictions. Even Nostradamus had his problems.
If I had to place a bet I would tilt toward gas and oil prices rising again relatively soon, but it is only a tilt and I wouldn’t put a lot of money on the table. I do believe the Saudis and OPEC will move to put a cap on production and try to increase prices in the relatively near future. They plainly need the revenue. They will risk losing market share. Russia’s oil production will move downward because of lack of drilling materials and capital generated by western sanctions. The U.S. economy has shown resilience and growth…perhaps not as robust as we would like, but growth just the same. While current low gas prices may temporarily impede sales of electric cars and replacement fuels, the future for replacement fuels, such as ethanol, in general looks reasonable, if the gap between gas prices and E85 remains over 20 percent — a percentage that will lead to increased use of E85. Estimates of larger cost differentials between electric cars, natural gas and cellulosic-based ethanol based on technological innovations and gasoline suggest an extremely competitive fuel market with larger market shares allocated to gasoline alternatives. This outcome depends on the weakening or end of monopolistic oil company franchise agreements limiting the sale of replacement fuels, capital investment in blenders and infrastructure and cheaper production and distribution costs for replacement fuels. Competition, if my tilt is correct, will offer lower fuel prices to consumers, and probably lend a degree of stability to fuel markets as well as provide a cleaner environment with less greenhouse gas emissions. It will buy time until renewables provide a significant percentage of in-use automobiles and overall demand.
It seems like a kind of Hollywood fantasy — autonomous little roadsters scooting in and out of traffic, breathlessly avoiding collisions and getting to their destination before anyone else.
Then again, it seems like the inevitable. If computers can perform medical diagnoses, accomplish instant translations for tourists and power Martian rovers, what’s so complicated about driving a car?
The self-driving car has gotten a lot of publicity lately. Google has a demonstration project and there have been the usual speculations about how long before self-drivers become a common sight. Four states have passed legislation allowing their operation and this month self-driving cars received the ultimate accolade of any new technology by being opposed by the Ralph Nader’s Consumer Watchdog, thereby joining fracking, nuclear power, GMO foods and other technological advances as being opposed by the Naderites.
Yet in truth, the idea of self-driving vehicles has been around for a long, long time. Experiments go back as far back as the 1920s. Engineers tried burying electric cables beneath the road to send signals that would keep cars on track. With the development of computers, however, research switched to autonomous vehicles with a dozen auto manufacturers and universities doing serious work.
In 1995, Carnegie Mellon University built an autonomous vehicle that traveled 3,100 miles cross-country for the “No Hands Across America” tour, with only minimal human intervention. In 2005, a Google vehicle equipped with 3D cameras, radar and a software package called Google Chauffeur won a $2 million prize in a Grand Challenge sponsored by the U.S. Department of Defense. In 2010, four self-driving vehicles designed at the University of Parma, Italy duplicated Marco Polo’s expedition by driving from Italy to China with only occasional intervention by their human drivers. Google’s fleet of a dozen self-driving cars has now logged 700,000 miles on public highways without experiencing any trouble. The only accident occurred when one of them was read-ended by another vehicle at a traffic light.
Indeed, as things stand now, the biggest obstacle to widespread adoption may be the predictable human reluctance to have the wheel taken out of their hands. One poll in Germany found that while 22 percent of respondents had a positive attitude toward driverless cars, 44 percent were skeptical and 24 percent were actively hostile toward the idea.
So aside from inspiring a hundred high school science projects and proving that computer geeks can do just about anything, what would be the advantage of self-driving vehicles? Here are a few of the possibilities:
Greater fuel efficiency: Advocates say that the precision achieved by automated vehicles in evening out traffic flows would cut down on national gasoline consumption. Instead of some cars dawdling in the fast lane while others weave in and out, traffic would follow a much more orderly pattern. Estimates are that a large fleet of self-driving vehicles could cut national fuel consumption by as much as 10 percent.
The advance of non-gasoline fuel systems: Since the experiments with trolley-like electronic tracks of the 1920s, self-driving systems have been associated with electric cars. While it will be perfectly possible to mount self-driving equipment on a gasoline-powered car, the “wave of the future” seems to be associated with non-gasoline vehicles. Google’s self-driver runs on electricity as do nearly all other experimental models.
Fewer accidents: Although humans may be reluctant to admit it, the vast majority of accidents are caused by driver error. The 360-degree visibility and unblinking vigilance of self-drivers could be a vast improvement. Many new cars are already beginning to incorporate some of the features with rear-view cameras and automatic braking. The 2014 Mercedes S-class offers options for self-parking, automatic accident avoidance and driver fatigue detection. One website that projects the self-driving future even suggests that the main job losses would be among: 1) hospital emergency room services, 2) auto repair shops and 3) trial lawyers specializing in auto accidents!
Peer-to-peer sharing of traffic information: The end point of self-driving would be a peer-to-peer information-sharing system whereby individual vehicles would be warned of congestion and traffic tie-ups and routed away from them. A 2010 study conducted by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration projected that an amazing 80 percent of all traffic accidents could be avoided by such a peer-to-peer system that smooth out traffic patterns and prevent cars from bumping into each other on congested highways.
More efficient traffic lights: How much time and gas is wasted by cars waiting for the light to change when no cars are coming in the crossing lane? Computerized systems linked to self-drivers could do wonders to hasten traffic flow and ease the time needlessly spent waiting for red lights.
Driving services for people who cannot drive: Many elderly and handicapped people cannot drive under ordinary circumstances, but could manage a vehicle in which they program it to tell it where they want to go. One of Google’s first early adapters was Steve Mahan, a California resident who is legally blind. This YouTube video shows him running a series of errands through his neighborhood, including a visit to a drive-in taco stand. All this might seem that it would increase driving and add to the nation’s fuel consumption until you consider that many of these people are already serviced by elaborate jitney systems that spend a great deal of time making empty runs. Once again, self-drivers would add precision and efficiency to the system.
Mass public transit — the possibility of a whole new personal mobility system: At the end point of this new technology is the vision of a whole new transportation system where far fewer vehicles would be needed to get people where they want to go. Driving this vision is the statistic that the average car is parked 90 percent of the time. If these vehicles could be put to more efficient use — something along the lines of bike-sharing on city streets — then the need for vehicles might be drastically reduced. Particularly in urban settings, more efficient matching of vehicles and passengers would cut down on the need for street parking. Uber, the San Francisco company that matches passengers with drivers of vehicles for hire, is now operating in 200 cities in 42 countries around the globe. The fuel savings it creates through matching efficiency are phenomenal.
Much of the fruits of these innovations are still in the future, but don’t put it past innovators like Google to make it happen quickly. In 2012 the Nevada Department of Motor Vehicles issued the country’s first license to a Toyota Prius modified with Google technology. Florida and Michigan have also issued permits for road testing. Next January, Google will launch 200 gumdrop-shaped vehicles completely void of steering wheel, brake and gas pedal that will begin cruising the streets of Mountain View, Calif., in an experiment supervised by the California DMV.
The future may be closer than we think.
Market Research Reports, Inc. has announced the addition of “Global Demand, Capacity and Prices for Methanol – China to Remain the Dominant Market” research report to their website.
Chinese shipyards are seeking to take about $10 billion in orders for new liquefied natural gas tankers over the rest of the decade, part of a plan to restructure the country’s ailing shipbuilding sector and secure China’s energy supply chain.